views

What Is Commercial Hvac And Types Of Hvac Systems For Commercial Buildings
Commercial HVAC systems (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) are designed to achieve the same goal as a domestic HVAC system. They provide high-quality, comfortable air at a temperature between 72 and 60 degrees Celsius and a range of humidity levels of 40-60 percent.
The heating of air is usually achieved by burning fuels (gas-electric or oil). Naturally, it is the reverse. This method draws heat from indoors and cools it with refrigerant or water-cooled units. It removes humidity.
Ventilation systems use fans to supply the outside air. Then, the indoor and outdoor air are passed through filters that filter out the contaminants and expel them from the building. The CO2 concentration remains below 1,000 molecules/million.
Ventilation systems that are well designed can reduce odours and diluviates gases, such as carbon dioxide. They also help prevent the spread of respiratory diseases. It is important because particles that aren't needed can make the air smelly, and promote the growth of mould and mildew.
What Is A Commercial Hvac System?
The temperature control in commercial buildings is dependent on three components: cool or warm, distribution and control. The thermostat controls the temperature of the cool air inside the building. It flows through the same conduits as the heated air. The source of cool air may be different.
Cold Or Warm Air
Heating is usually turned on in commercial HVAC systems. The furnaces produce combustion gas which is then transferred to a heat exchanger, where it warms the air. Heat pumps sometimes transfer outdoor heat indoors. Although air conditioners work in the same way as heat pumps, they also transfer indoor heat outdoors.
Some commercial buildings use boilers to heat their water. The pipes are used to heat the hot water through the ceilings, floors and walls. Although it is not evident that the building is heating, you will feel the warmth from the air.
Distribution
Learn more about mechanical systems that circulate air in buildings by allowing ventilation. Warm air ascends and cool air fall is an example of this concept. In some cases, the system may cause an outflow of air that has been modified in thermal terms.
Controls
Commercial buildings can use simple, programmable thermostats to regulate this. They will send different heating and cooling schedules throughout the day, much like residential HVAC systems.
Direct Digital Controls (DDC), which can be used in commercial HVAC systems, are often more complex. Advanced controls can be used to increase energy efficiency and reliability in commercial structures. Sensors are used by central computers to automate lighting and temperature control.
Staff can respond to requests and change settings from their main computer. Users can receive performance updates, troubleshoot issues and perform maintenance from their main workstation. It is the most expensive option because of its adaptability and sophistication.
Temperature setbacks can be used to reduce energy consumption by using simple controls or DDC. Temperature setbacks are defined as the time periods when no cooling or heating is needed. For example, the temperature setbacks could be used to determine when a day's work can be done in an empty space.
You're right! Now you know how an HVAC system works.
Types Of Hvac Systems For Commercial Buildings
Packaged Systems
Packaged systems include the fan coil, compressor, compressor and evaporator. It also includes the thermostat. For those with limited space, packaged HVAC units can be used.
Packaged terminal air conditioners are usually installed in window-mounted hospitals, condominiums, and senior residences. These structures require that their residents control the temperature and quality of the air.
Packaged terminal heat pump can be used to heat and cool, by transferring heat from outside to inside in winter and vice versa during summer.
Split Systems
Split Systems are connected to the building's air ductwork like a home. Split Systems are ideal for residential properties. They can also be used in smaller commercial spaces, such as small offices and restaurants. The thermostats and DDC control each space.
But what about the downside? Separate HVAC units may be required for each room that you want to have heat controlled. These can block the roof or other spaces around the building. Although zoning can be used for space regulation, it is costly.
A variable refrigerant method (VRF) is a way to heat and cool multiple parts of large commercial structures. VRF systems are not well-known in the US so they aren't widely used. They use heating systems also known as heat pumps. They heat the air in one area and cool it. Then they transfer it to another location. This technique will be discussed in more detail in the future.
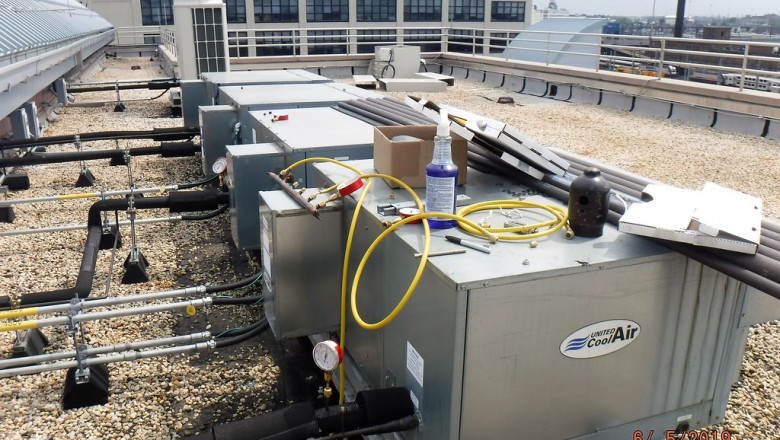
Rooftop RTU HVAC
A rooftop unit (also called an RTU) is a type unit that is found on the roof. Weatherproof housings protect the main components of roof-mounted HVAC units due to their location in flat roofing (no more than 10 levels above). This compact unit includes the compressor, condenser and evaporator, as well as a blower.
Air handlers are fully built from factory rooftop units. The air it circulates through ducts is changed. Some RTUs are heat- and cool-only, others only heat or cool, while others combine both.
The RTU's rectangular case contains an air hood, which allows for the adjustment of the outside air. Air is forced through dampers, which are rotating sheets that regulate airflow and move them through a filter. Then it is pushed through the coils used to heat or cool the air. After sucking air, the fan blasts it into the duct system which transports it to the desired area.
An RTU, in general, is a mixture of indoor and outside air. This allows for CO2 to remain at a safe level. It also helps conserve energy by not overloading the unit when it's extremely cold or hot.
Pros
-
Simple and flexible
-
HVAC units that are fully assembled and integrated
-
You can get better results with zoned HVAC (each RTU only takes care of one area of the building).
-
Affordable
-
It is easy and simple to install
-
Quiet
-
Saves floor space
-
More secure location
-
New models that are more efficient
Cons
-
It's not as durable as
-
Older models use less energy, which can lead to higher utility bills.
-
More attention is needed
RTUs are extremely popular but there is another option for your building.
VRF Systems
The US still uses VRF systems very rarely. VRF systems were first developed in Japan in the 1980s. They are highly advanced HVAC systems that can be used commercially.
VRF systems, as the name implies, are ductless. Instead, they rely on heat pump systems or heating recuper units that pump refrigerant to an outdoor central unit. This housed all the compressors and condensers. Temperature at which each zone becomes depends on how quickly indoor units are refrigerated.
VRF systems' quiet indoor components take up very little space. The indoor components can also be easily set up and removed using an elevator. There is no need to install ductwork.
VRFs are up to 30% more efficient than traditional ducted HVAC systems. Because of the variable compressor speeds, VRFs can adjust temperature more accurately than traditional ducted HVAC systems. Additionally, ductwork is not wasted as much as traditional systems.
VRF systems are more expensive and need an extra condenser in case of malfunction.
Commercial HVAC systems need to be robust, durable, and have complex connections and moving parts.
It is not simple to understand.
This guide is a great place to start. Now you know what to watch out for and how avoid costly problems. If you notice something amiss, it's a good idea to contact a professional. They will ensure your Commercial HVAC systems is in top form.