views
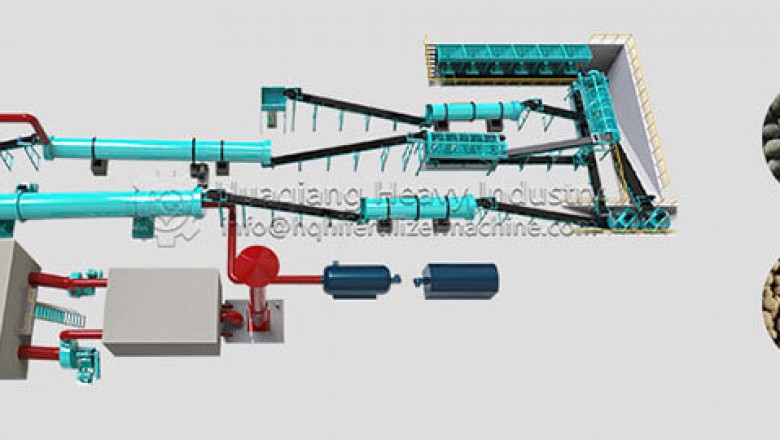
Formulation technology of NPK compound fertilizer production line
When NPK compound fertilizer production line makes powdery materials into granules, the viscosity of the materials must be considered. Only when the materials have enough viscosity can the dispersed materials be agglomerated into granules.
First of all, the existing chemical fertilizer varieties are classified, which have good viscosity and which have poor viscosity. We call the materials with good viscosity as viscous materials, and the materials with poor viscosity as sandy materials.
Next, we classify and quantify the viscosity and sand properties of materials to achieve operability.
Sticky materials have the following varieties: Ordinary superphosphate, diammonium phosphate, monoammonium phosphate, and heavy calcium.
Sandy materials have the following varieties: potassium chloride, potassium sulfate, ammonium chloride, ammonium sulfate.
The compatibility of ammonium bicarbonate and superphosphate can reduce the viscosity of superphosphate, while the compatibility of ammonium bicarbonate and monoammonium can improve the viscosity of Monoammonium. Although the dosage of ammonium bicarbonate in the formula is generally small, the duality of ammonium bicarbonate should also be paid attention to.
Urea is between viscosity and sand.
The granulation must meet the viscosity standard
A. When using calcium superphosphate as phosphorus source, calcium superphosphate plus viscous conditioner is more than 50%
B. When ammonium phosphate is used as phosphorus source, ammonium phosphate plus viscous conditioner is more than 40%
C. The formula containing urea should be determined according to the amount of urea. The high nitrogen formula has a large amount of urea. Generally, the proportion of viscous materials can be appropriately reduced to about 35%.