views
Developed countries, including Germany, the US, and Japan, are focusing on increasing the use of environmentally-friendly products instead of petroleum-based products. The European Union (EU) has been preferring the use of such products more than the US and Japanese governments. It insists on the use of bio-based materials, encouraging recyclability of vehicle components, or making the automotive manufacturers responsible for disposal at the end of the service life of the vehicles.
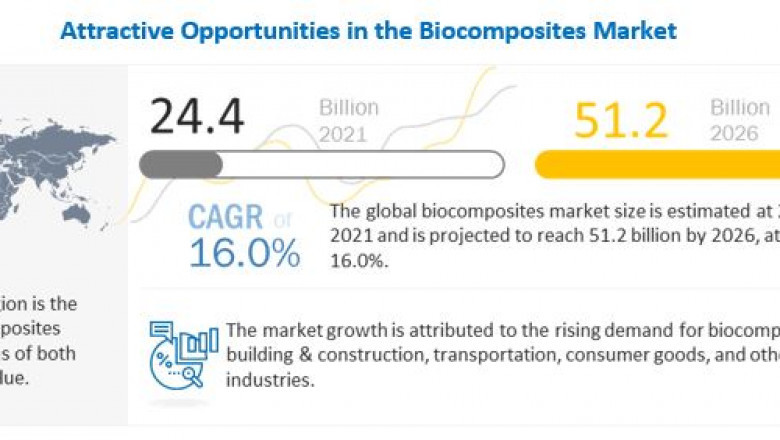
The global biocomposites market size is expected to grow from USD 24.4 billion in 2021 to USD 51.2 billion by 2026, projecting a CAGR of 16.0% during the forecast period between 2021 and 2026. The major biocomposite manufacturers are UPM (Finland), Trex Company (US), Fiberon LLC (US), FlexForm Technologies (US), Universal Forest Products, Inc. (US), Nanjing Jufeng Advanced Materials Co., Ltd (China), Meshlin Composites ZRT (Hungary), Tecnaro GmbH (Germany), among others. These companies have adopted various organic and inorganic growth strategies.
However, the requirements in North America are not as stringent for automotive manufacturers as they are in other markets around the world. For example, the Japanese government has a target of replacing 25% of plastic consumption with renewable products, by 2030.
According to the EU Commission, every year, the European car industry consumes 80,000 tons of plant and wood fibers to reinforce composite products instead of other synthetic fibers. The European Union (EU) has also emphasized, on using recyclable and biodegradable parts for automotive interior components. This would boost the use of biocomposites in the transportation end-use industry during the forecast period. These regulations are expected to increase the demand for biocomposites in transportation, building & construction, electrical & electronics, among other end-use industries.












