views

The pandemic has disrupted healthcare systems worldwide, with hospitals being overwhelmed due to the increasing influx of patients. Temporary hospitals are also being set up to deal with the growing number of cases. Hence, the spread of COVID-19 has spurred a surge in demand for HAI services due to the growing cases of HAIs in hospital settings.
With the current COVID-19 pandemic wreaking havoc across the globe, various measures are being taken by companies as well as government bodies to drive market growth. For instance, the FDA has recommended that Sterigenics should reopen its ethylene oxide-based sterilization plant in the US. The plant had been shut due to harmful emissions, which were believed to be carcinogenic. In March 2020, the company received permission to reopen the plant for 21 days to sterilize PPE for healthcare workers to use during the COVID-19 pandemic. Such developments are anticipated to drive the growth of this market.
Equipment sterilization plays a critical role in preventing the spread of COVID-19 in healthcare settings. During the outbreak, patient-to-patient pathogen transmission via medical devices can be entirely prevented by properly sterilizing medical devices. The usage of reprocessed equipment to disinfect or sterilize medical devices is higher than normal during the pandemic since improper decontamination of surgical instruments, endoscopic devices, respiratory care devices, and reusable hemodialysis machines can increase the chances of COVID-19.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=204343466
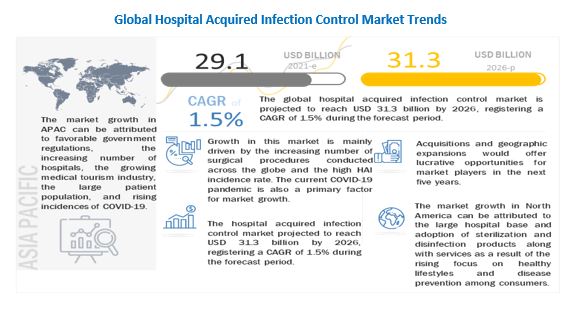
With the COVID-19 outbreak, there has been an unprecedented global demand for advanced healthcare facilities, services, and infrastructure to treat infected patients. With the considerable rise in the cases of COVID-19 across the globe, the number of patient admissions in hospitals has increased significantly, leading to an increase in the demand for disinfection and sterilization measures. With the prevalence of many epidemics and pandemics around the world, the government bodies of numerous countries are ramping up their healthcare infrastructure to tackle any outbreak. Better reimbursement policies for every citizen to get good healthcare facilities are also helping more people get treatment in hospitals. This aspect eventually boosts the growth prospects of the hospital acquired infection control market.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has affected the hospital sector more than any other end user segment. According to a survey conducted by the US Department of Health and Human Services (between March 23 and March 27, 2020), hospitals in the US reported a shortage of specialized providers needed to meet the anticipated patient surge.
It also raised concerns that staff exposure to the virus may exacerbate staffing shortages and work overload. Factors such as the increasing demand for hospital beds and ICUs in countries with an increasing incidence of COVID-19 and an increasing number of temporary hospitals are driving the demand for disinfectant and sterilization products and services. Infrastructural expansion is evident globally as governments work to combat the virus and care for an increasing number of patients.
Healthcare providers reprocess reusable medical devices to save money and reduce waste. Examples of reusable medical devices include surgical forceps, endoscopes, and stethoscopes. However, there are concerns about the safety and performance of reprocessed devices.
The debris can allow microbes to survive the subsequent disinfection or sterilization process, which could then lead to HAIs. Inadequate reprocessing can also result in other adverse patient outcomes, such as tissue irritation from residual reprocessing materials such as chemical disinfectants. These factors are limiting the acceptance of reprocessing among hospital administrators and physicians.
The debris can allow microbes to survive the subsequent disinfection or sterilization process, which could then lead to HAIs. Inadequate reprocessing can also result in other adverse patient outcomes, such as tissue irritation from residual reprocessing materials such as chemical disinfectants. These factors are limiting the acceptance of reprocessing among hospital administrators and physicians.
The prominent players in hospital acquired infection control market are STERIS plc (US), Sotera Health Company (US), Getinge AB (Sweden), Advanced Sterilization Products (ASP) (US), Ecolab Inc. (US), 3M Company (US), MATACHANA GROUP (Spain), MMM Group (Germany), Belimed AG (Switzerland), Reckitt Benckiser (UK), Metrex Research LLC (UK), Miele Group (Germany), Pal International (UK), MELAG Medizintechnik GmbH & Co. KG (Germany), Contec, Inc. (US), MEDALKAN (Greece), Systec GmbH (Germany), C.B.M. S.r.l. Medical Equipment (Italy), Continental Equipment Company (US), and BGS Beta-Gamma-Service GmbH & Co. KG (Germany).












