views
Part A of Medicare
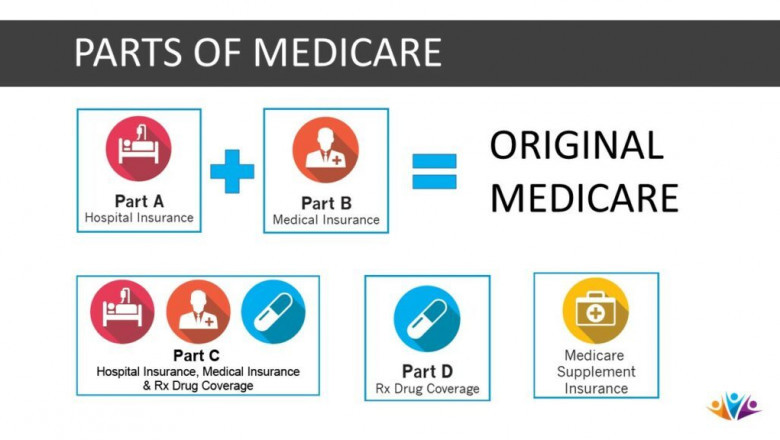
Original Medicare is divided into two parts: Medicare Part A (hospital insurance) and Medicare Part B (medical insurance) (medical insurance). Medicare Part A covers inpatient care, which includes treatment obtained in a hospital, skilled nursing facility, or, in some cases, at home.
Most persons are immediately eligible for Medicare Part A at the age of 65 if they are already receiving Social Security or Railroad Retirement Board payments. If you have a handicap, end-stage renal disease (ESRD), or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, you may be eligible for Medicare Part A before the age of 65. (ALS). You must be a US citizen or a lawful permanent resident of the US for at least five years.
In general, Medicare Part A coverage includes:
• Inpatient hospital care
• Limited home health services
• Skilled nursing facility care, provided that custodial care is not the primary care necessary
Please keep in mind that some of the aforementioned advantages are only available in particular situations and under certain conditions.
Hospitalization under Medicare Part A
As a Medicare Part A beneficiary, you will be covered for hospital expenditures related to your inpatient care, such as a semi-private room, meals, nursing services, drugs prescribed as part of your inpatient treatment, and any other hospital services and supplies. Inpatient treatment provided by:
• Acute care hospitals
Inpatient treatment provided by:
• Acute care hospitals
• Critical access hospitals
• Inpatient rehabilitation facilities
• Long-term care hospitals
• Mental health care
• Enrollment in an eligible clinical research study
Please keep in mind that Medicare Part A hospital insurance does not cover the price of a private room (unless medically essential), private-duty nurses, personal care goods such as shampoo or razors, or other incidentals such as telephone and television.
Medicare Part A home health care benefits
Home health care services are covered under Medicare Part A if they are judged medically essential and prescribed by your doctor.
Home health care services may include the following: • Part-time or intermittent skilled nursing care • Physical therapy • Speech-language pathology services • Occupational therapy
• Home health aide services on a part-time or intermittent basis
• Long-lasting medical devices, if ordered by your doctor*
*This expense is reimbursed separately under Medicare Part B if your doctor orders durable medical equipment as part of your care and the device fulfils eligibility conditions. If you qualify, Medicare will normally reimburse 80% of the Medicare-approved cost for durable medical equipment.
Nursing home coverage under Medicare Part A
After a qualified hospital inpatient stay for a connected sickness or accident, skilled nursing facility (SNF) stays are covered under Medicare Part A. To be eligible for SNF treatment, you must stay in the hospital for at least three days, commencing on the day you are initially admitted as an inpatient. The day you are discharged does not count against the three-day minimum. Time spent as an outpatient under observation does not count either.
A Medicare-certified institution must offer competent nursing care. Skilled nursing care covered by Medicare includes, but is not limited to:
• Semi-private room
• Meals
• Skilled nursing care
• Rehabilitation services, if medically required to address your sickness; and
• Medical social services.
• Medications administered while in SNF care
• Medical supplies and equipment utilised in SNF
• Ambulance transported to nearest provider if needed treatments are not offered at the SNF
Your doctor must certify that you require daily expert care that you are unable to obtain at home, such as IV medicines or physical therapy. Long-term care is not covered by Medicare Part A. (or personal care, if that is the only care you need).
Hospice treatment under Medicare Part A
If your doctor has verified that you have a terminal disease with a life expectancy of six months or fewer, you may be eligible for hospice care. The emphasis of hospice care is on palliative care rather than treating your sickness. The objective is to make the patient as comfortable as possible while relieving pain.
You must fulfil all of the following requirements to be eligible for Medicare-covered hospice care:
• You must be enrolled in Medicare Part A.
• Your doctor or health care provider must certify that you are terminally ill with a life expectancy of six months or less.
• You must agree to forego curative therapies for your terminal disease; nevertheless, Medicare will continue to pay palliative (comfort-focused) treatment for your terminal illness, as well as associated symptoms or conditions. Hospice treatment must be provided by a Medicare-approved hospice institution.
Hospice care under Medicare Part A is often provided at the patient's home. It may include, but is not limited to:
• Doctor services
• Nursing care
• Pain relief drugs
• Social services
• Durable medical equipment
• Medical supplies
• Homemaker services
• Physical and occupational therapy
• Dietary counselling
• Short-term inpatient care (if needed for pain or symptom management)
• Short-term respite care
If a patient is receiving hospice care, Medicare Part A may cover some charges that Medicare does not ordinarily cover, such as spiritual and bereavement counselling.
Medicare Part A only covers hospital room and board if the hospice medical team approves short-term inpatient stays to treat pain or other symptoms.
Medicare Part A Eligibility
In general, you are eligible for Medicare Part A if you are:
• 65 or older;
• a U.S. citizen or permanent legal resident for at least five years; and
• receiving retirement benefits.
• You have a handicap and are getting disability benefits.
• You have advanced renal disease (ESRD).
• You have amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, often known as Lou Gehrig's disease).
Most beneficiaries do not have to pay a Medicare Part A premium if they have worked for at least ten years (or forty quarters) and paid Medicare taxes throughout that period.
Individuals who are not eligible for premium-free Medicare Part A can nonetheless enrol and pay a premium for Part A. Beneficiaries who postpone enrolling after becoming eligible for Medicare Part A may face a late enrollment penalty once they do join up.
Initial Medicare Part A Enrollment
Enrollment in Medicare Part A is normally automatic if you reach 65 and are already receiving Social Security retirement benefits or Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) payments. Medicare Part A benefits begin on the first of the month after you reach the age of 65. If your birthday falls on the first of the month, your benefits will start the month before you reach the age of 65. If you registered in Medicare Part B when you applied for retirement, your Part B coverage will begin at the same time as your Part A coverage. About three months before your 65th birthday, you will get your red, white, and blue Medicare card.
If you do not qualify for Social Security retirement benefits or Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) payments, you must manually enroll in Medicare Part A during the Initial Enrollment Period (IEP). You can do so by visiting the Social Security website, visiting a local Social Security office, or phoning (855)658-0323 from 7 a.m. to 7 p.m., Monday through Friday.
The IEP lasts seven months, beginning three months before your 65th birthday and ending three months later. The month you enrol during your IEP determines when your coverage begins. If you do not enrol during your seven-month IEP, you must wait until the following general enrollment period (January 1 to March 31) to enrol.
After collecting Social Security disability payments for 24 months, you will be eligible to enrol in Medicare Part A hospital insurance (and Medicare Part B medical insurance). In the 25th month, your coverage will begin. Your Medicare card will arrive around three months before the start of your coverage.
If you have ALS (Lou Gehrig's disease), your Medicare Part A hospital insurance (and Medicare Part B medical insurance) will begin the same month as your Social Security benefits. Your Medicare card will be mailed to you around one month after you apply for Social Security disability benefits.
If you have end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and need dialysis, your Medicare effective date is generally the first day of the fourth month of dialysis. However, you must apply for Medicare benefits; if you are under the age of 65, you will not be automatically enrolled.
Part A Medicare deductible in 2022
You must pay some expenses under Medicare Part A. Most consumers do not have to pay a monthly Part A premium. You may be required to pay coinsurance and/or copayments. Part A costs can be found here.
The Part A deductible is not calculated on an annual basis. It's "per benefit period" instead.
A benefit period begins the day you are admitted as an inpatient to a hospital or skilled care facility. It expires after you have not received inpatient care for 60 consecutive days. If you spend a lot of time in the hospital, you may have to pay numerous Part A deductibles in one year.
In 2022, the Medicare Part A deductible is $1,556.
Would you want to look into some of the Medicare plans that are available in your area? Simply put your zip code into the box on this page to generate a list and begin comparing plans.












