views
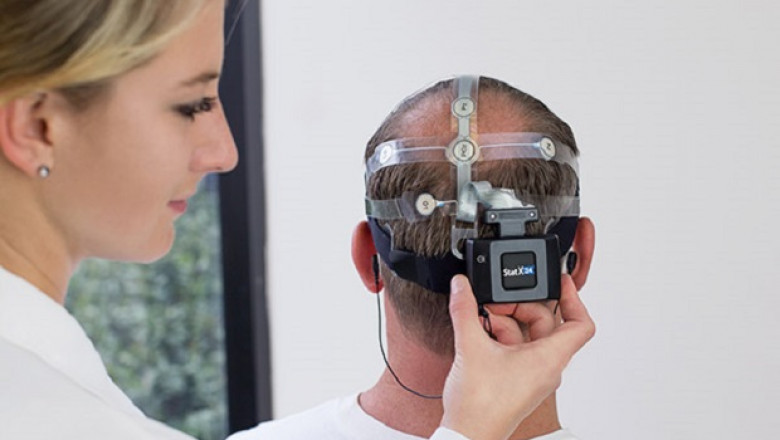
Brain monitoring, often known as brain monitoring, is a technique that allows clinicians to track brain activity using head-worn equipment such as a cap with sensors that can detect electrical activity in the brain. Furthermore, brain monitoring devices aid in the detection and measurement of irregularities in the functioning of brain cells linked to neurological disorders like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, epilepsy, dementia, multiple sclerosis, brain tumours, and more. As a result of the rising prevalence of the aforementioned illnesses, the demand for brain monitoring has increased.
According to the Alzheimer's Association, more than 1.5 million people in Germany have Alzheimer's disease, and over 44 million people worldwide have dementia, making it a global health problem that must be addressed. As a result, the demand for brain monitoring rises. Researchers at Carl von Ossietsky University in Oldenburg, Germany, successfully tested a brain-monitoring gadget that could replace traditional encephalography in June 2020. (EEG).
Brain monitoring helps avert harmful effects by monitoring functions like electrical and neural activity, blood flow, cerebral oxygen capacity, pressure surrounding the brain, tumour, gravity neighbouring the brain, traumatic brain injury, and other problems. With bilateral data collecting and processing of EEG (Electroencephalography) signals, doctors may monitor the status of the brain under anaesthesia, which aids in anaesthetic management. EEG is a non-invasive method for measuring brain electrical activity.
Brain monitoring also aids clinicians in determining and administering the exact amount of medication required to fulfil the unique needs of each patient. Traditional brain monitoring techniques are supplemented by continuous brain tissue oxygen (PbtO2) monitoring. It is an invasive procedure that involves inserting a catheter into the brain parenchyma to assess the oxygenation of brain tissue. In the intensive care unit, the oxygenation level of brain tissue is an important metric. In urgent clinical settings where the amount or progression of neurologic damage is uncertain, brain monitoring is essential.
Read More @ https://digitalcmiinsights.blogspot.com/2021/09/brain-monitoring-used-to-assess.html
Sources @ https://www.openpr.com/news/1185931/brain-monitoring-market-opportunity-analysis-2018-2026.html