views

The COVID-19 outbreak is an unprecedented global public health challenge and is expected to have a significant impact on the blood collection devices market.
Both hospital and independent laboratories are generally reviewing each test to decide whether to recommend consultations with laboratory hematologists for tests with a higher risk profile or not offer tests that could not be performed safely. This affected the market negatively in the first few months of the pandemic, reducing the use of blood collection devices. However, increasing caution and the rising testing volumes, along with the need for regular health and body checkups will ensure market growth in a later phase.
Results now take an average of four to six days for the general population, much longer than the two to three days required before. This is because tests for hospital patients and symptomatic healthcare workers are prioritized and take one day on average, which has resulted in a delayed cycle. While it has affected market growth to some extent, the situation is expected to change for the better.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=39733117
The rising prevalence of infectious diseases such as hepatitis B (HBV), hepatitis C (HCV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), malaria, syphilis, and brucellosis are a major factor driving the demand for effective blood collection (due to the risk of disease transmission during blood transfusion). According to the WHO (July 2021), there were an estimated 37.7 million [30.2–45.1 million] people living with HIV at the end of 2020, over two-thirds of whom (25.4 million) are in the WHO African Region.
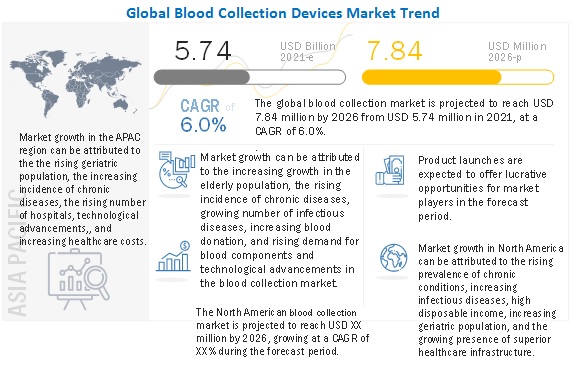
The burden of chronic diseases is rapidly increasing worldwide. Almost half of the total chronic disease deaths are attributable to cardiovascular disease (CVD). In the US alone, as per the American Heart Association, the prevalence of CVD is projected to increase from 36.9% in 2010 to 38.7% by 2020 and 40.5% by 2030. Obesity and diabetes are also showing worrying trends, not only because they already affect a large proportion of the population but also because they have started to appear earlier in life. The prevalence of lifestyle diseases is also growing across the globe, and particularly in emerging countries.
This scenario has ensured greater adherence to health checkups and the growing importance of markers to find disease conditions mainly via blood collection. Health checkups are gaining popularity both at a personal level as well as performed at a corporate level for employee well-being. This will be favorable for the market growth and a significant contributor to the blood collection devices market, as blood tests are a primary mode of diagnosing these diseases.
The cost of providing apheresis therapy is a matter of almost universal concern. Estimates of costs of individual apheresis treatments are very much available but vary widely. For instance, in the US, the cost of an apheresis procedure is approximately USD 2,500 per treatment. An investment of USD 19,000 to USD 32,000 for a blood cell separator is the initial cost for setting up the machine, and disposable sets produced by manufacturers will vary between USD 40 and USD 90 per treatment.
Owing to their high costs, the adoption of these automated blood collection products is very low as compared to manual blood collection products in countries such as China and India. This is limiting the overall growth of the blood collection devices market.
Collecting blood samples from patients with difficult venous access (DVA) is challenging or sometimes impossible. In DVA patients, traditionally used blood collection products are often unable to collect adequate samples, which can also lead to repeated attempts to collect blood. This increases the risk of anemia in patients and the risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens to nurses and phlebotomists.
Some of the key players include Becton, Dickinson and Company (US), Terumo BCT (US), Fresenius Kabi AG (Germany), Grifols S.A.(Spain), Haematonics (US), Nipro Medical Corporation (Japan), Greiner Holding (Austria), Quest Diagnostics (US), SARSTEDT AG & Co. (Germany), Macopharma (France), Smiths Medical (US), Cardinal Health (US), and Retractable Technologies (US).












