views
All You Need to Know About Cyber crime India
Crime is not new to all of us. Since the period humans have lived, crime has existed. They go hand in hand. The essence of crime has shifted over the passing of years, and so have the society and the people. With time, new technologies have become a crucial part of people's life. And with new technologies, new crime has begun to happen through these technologies.
Such a crime is known as Cyber Crime. According to the ancient texts, crime is an act committed by a person against another person. However, the definition is different in the context of cyber crime India. Such an act can be committed against an individual by any individual, firm, or group of people, like an organisation using technology.
Cyberspace is a virtual platform where people can compile information, communicate, etc., without restrictions.
Why is cyber crime deemed a severe offence?
Several privacy suspicions encircle cyber crime when susceptible information is intercepted and circulated to the public, legally or otherwise. Some of that information may comprise military deployments, internal government communications, and even private data about high-value individuals.
After knowing what is cyber crime in India, it is crucial to know that cybercrime is not constrained to individuals independently. Internationally, both governmental and non-state actors confront cybercrimes, encompassing espionage, monetary theft, and other cross-border crimes. Cybercrimes crossing international borders and implicating the actions of at least one nation-state are usually referred to as cyberwarfare.
In 2018, research by the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), in collaboration with McAfee, a major cybersecurity firm, concluded that shut $600 billion, nearly 1% of global GDP is reduced to cybercrime annually.
Laws against cybercrime in India
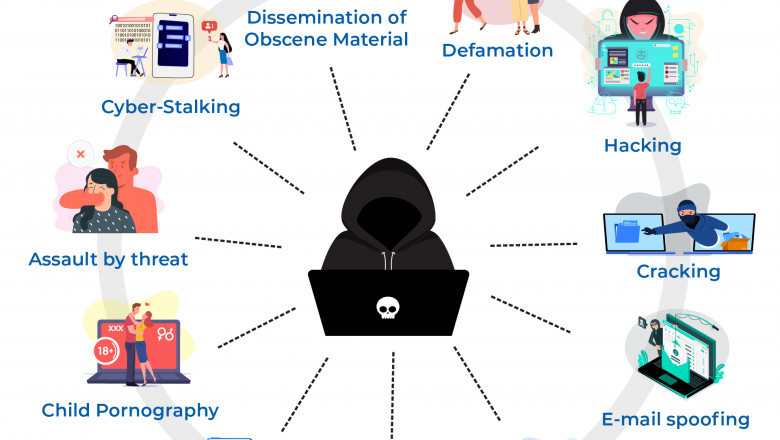
With the introduction of cyber laws in India, the Information Technology Act (IT Act) 2000 put down several types of crimes under cyber law in India. The following categories of cybercrimes come under the IT Act 2000:
Identity Theft: Identity theft is the theft of personal input of an individual to use financial services or theft of the financial assets themselves.
Cyber-terrorism: Cyberterrorism is known to cause severe harm or extortion of any facet subjected towards an individual, groups of individuals, or governments.
Cyber Bully: Cyberbullying is the act of coercing, defaming, harassing, or any other aspect of mental degradation through electronic means or modes such as social media.
Hack: Access to data through fraudulent or unethical ways is known as hacking. It is the most widespread form of cybercrime known to the general public.
Defamation: While everyone has a right to speak on internet platforms, if arguments cross a line and damage the reputation of any individual or group of people, they can put charged under the Defamation Law.
Trade Secrets: Internet organisation consumes a lot of their time and money on creating software, applications, and tools and depend on Cyber Laws to safeguard their data and trade confidences against theft, executing a punishable crime.
Freedom of Speech: In an era of the internet, there is a thin line between being a cyber-offender and using your freedom of speech and expression. As freedom of speech enables individuals to recite their minds, cyber law abstains from obscenity and crassness over the net.
Harassment and Stalking: Harassment and stalking are also forbidden over internet platforms. Cyber laws safeguard the victims and prosecute the offender against this offence.
IT Act, 2000 went through the amendments under the Indian Penal Code, 2008. These got formulated in light of the laws on cyber crime – IT Act, 2000 by the IT Act, 2008. They were implemented at the beginning of 2009 to enhance cybersecurity laws. Now that we thoroughly understand what is cyber crime in India, let’s aware our friends and family about it to stop such crimes.
Conclusion
Cyber crime India, also known as computer crime, is an illegal activity encompassing a computer or network-connected device, such as a mobile phone. The Department of Justice distributes cybercrime into three categories: crimes in which the computing device is the mark, for example, to acquire network access; crimes in which the system is used as a weapon, for example, to undertake a denial of service (DoS) attack; and crimes in which the computer is assigned as an accessory to a crime, for example, using a computer to stock illegally-obtained data.












