views

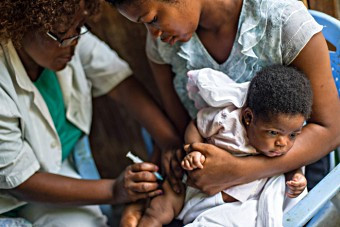
A vaccine is a biological preparation that, when administered, stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies against the agent used to make the vaccine. In order to form a vaccine, the disease-causing microorganism is typically weakened or killed. Microorganisms (bacteria or viruses) are grown on culture medium and then inactivated with heat and/or chemicals to create inactivated vaccines (formalin is mostly used for inactivation). As a result, the inactivated vaccine's components are unable to replicate.
Many non-governmental organisations around the world are raising awareness and providing low-cost immunisation to the population, which is expected to drive growth in the global inactivated polio and rabies vaccines market over the forecast period. For example, many low-income countries' populations, who cannot afford the full cost of vaccination, are supported by an external source to ensure that the population receives vaccination.
Read more @ https://cmisearchblog.blogspot.com/2022/03/inactivated-polio-and-rabies-vaccines.html












